Blog > A Guide for Arborist Service
Common Tree Diseases in Louisville, KY: Identification and Prevention Tips
Louisville is home to a wide variety of beautiful trees, from the stately oak to the picturesque dogwood. However, these trees can be susceptible to several common diseases that can compromise their health and longevity. By understanding these diseases and implementing effective prevention strategies, homeowners and gardening enthusiasts can help maintain the health of their landscape. Here, we’ll explore some of the most prevalent tree diseases in Louisville and offer practical tips for preventing them.

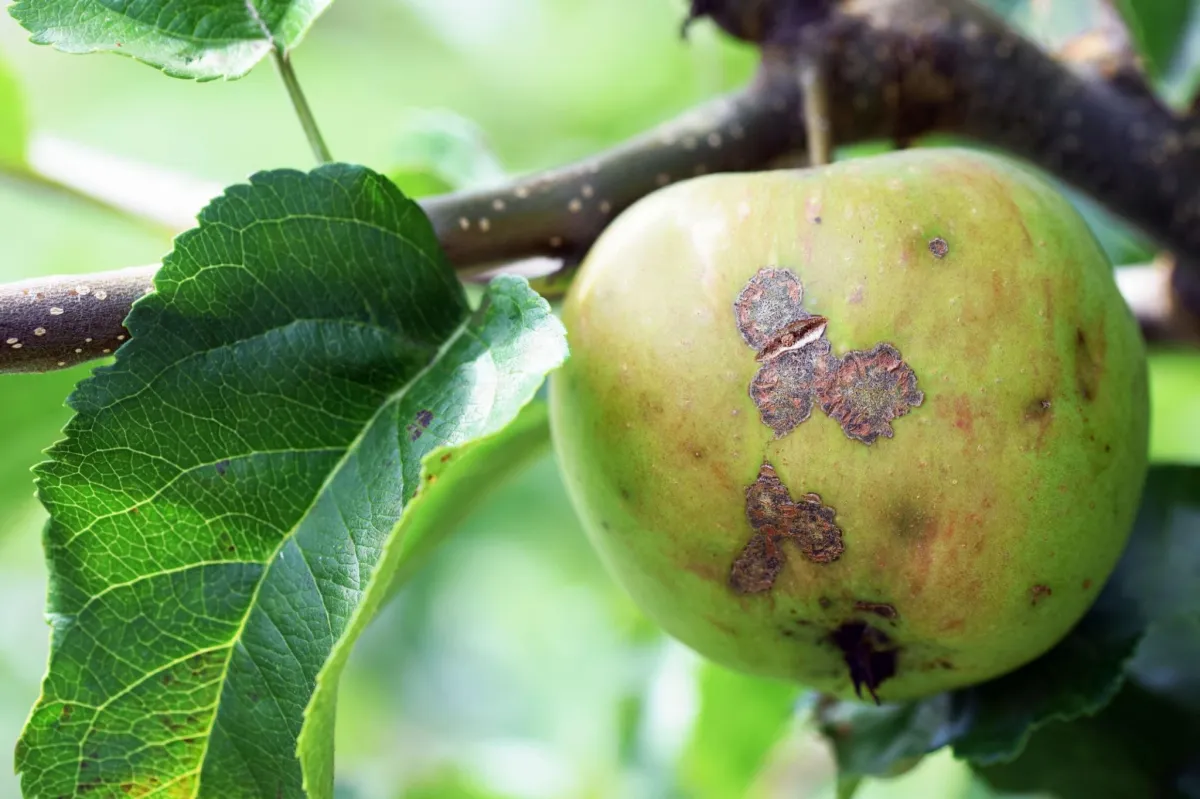
Apple Scab
Apple Scab primarily affects crabapple and apple trees, which are common in Louisville's residential areas. It is caused by the fungus Venturia inaequalis. The most noticeable symptoms include olive-green to dark brown spots on leaves, which can cause them to yellow and drop prematurely. Fruit may also show similar spots and become deformed.
Prevention tips:
Choose Resistant Varieties:
When planting new trees, opt for varieties that are resistant to apple scab.
Proper Sanitation:
Regularly clean up fallen leaves and debris around the tree base to minimize the spread of spores.
Adequate Spacing and Pruning:
Ensure trees have sufficient space and air circulation to dry leaves quickly, reducing the risk of infection.
Powdery Mildew
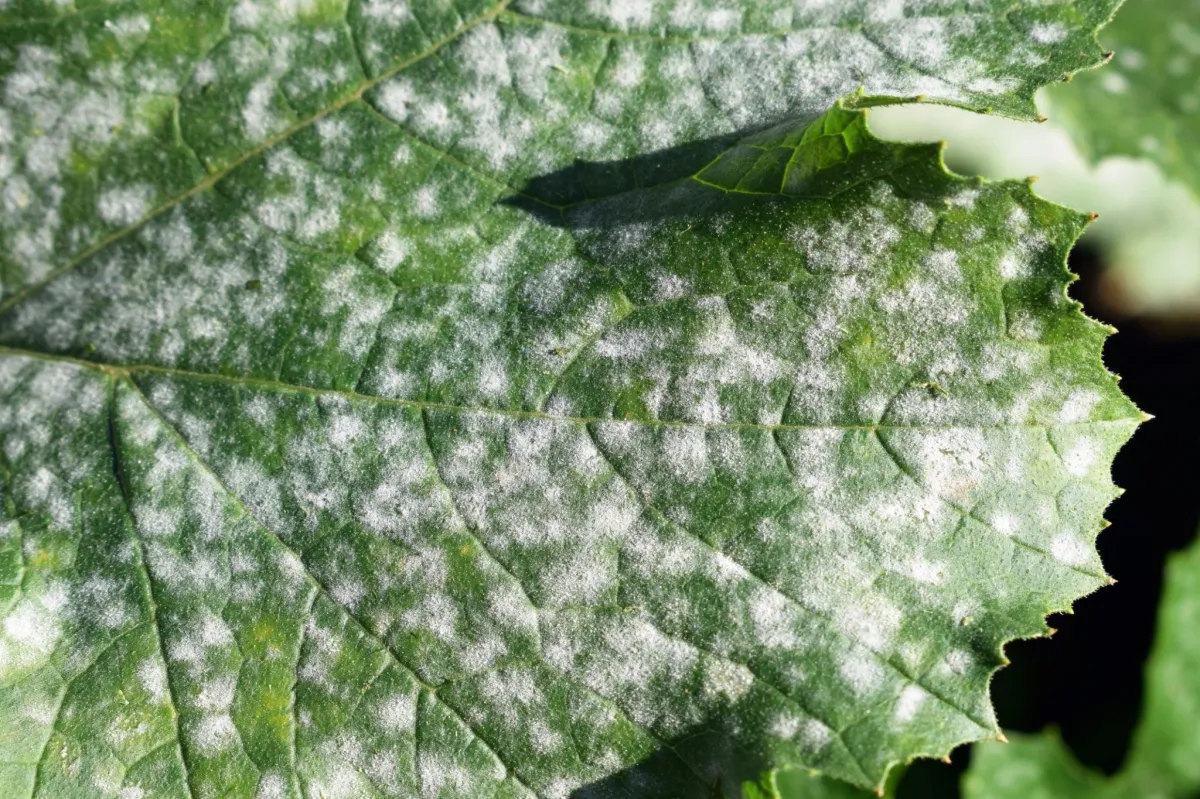

Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that forms a white or gray powdery coating on the leaves and stems of a variety of trees, including dogwoods and maples. While it rarely kills a tree, it can weaken it by inhibiting photosynthesis.
Prevention tips:
Sunlight and Air Circulation:
Plant trees in areas with full sunlight and good air circulation to reduce humidity around the foliage.
Avoid Overhead Watering:
Water the base of the tree to avoid wetting the leaves, which can promote fungal growth.
Fungicidal Sprays:
If necessary, apply fungicidal sprays early in the season to prevent severe outbreaks.
Oak Wilt

Oak wilt is a serious disease that affects oak trees, caused by the fungus Bretziella fagacearum. Symptoms include wilting, bronzing, and shedding of leaves, often starting at the crown and progressing downward. Red oaks are particularly susceptible and can die within a season of infection.
Prevention tips:
Avoid Pruning in Spring and Summer:
Since the disease spreads through open wounds and is carried by beetles active in these months, it’s best to prune oaks in the dormant season.
Monitor and Remove Infected Trees:
Quickly removing infected trees can prevent the spread of the disease to healthy trees nearby.
Use Fungicides or Tree Injections:
Professional arborists can apply these treatments to protect high-value oaks or prevent the spread in high-risk areas.
Anthracnose
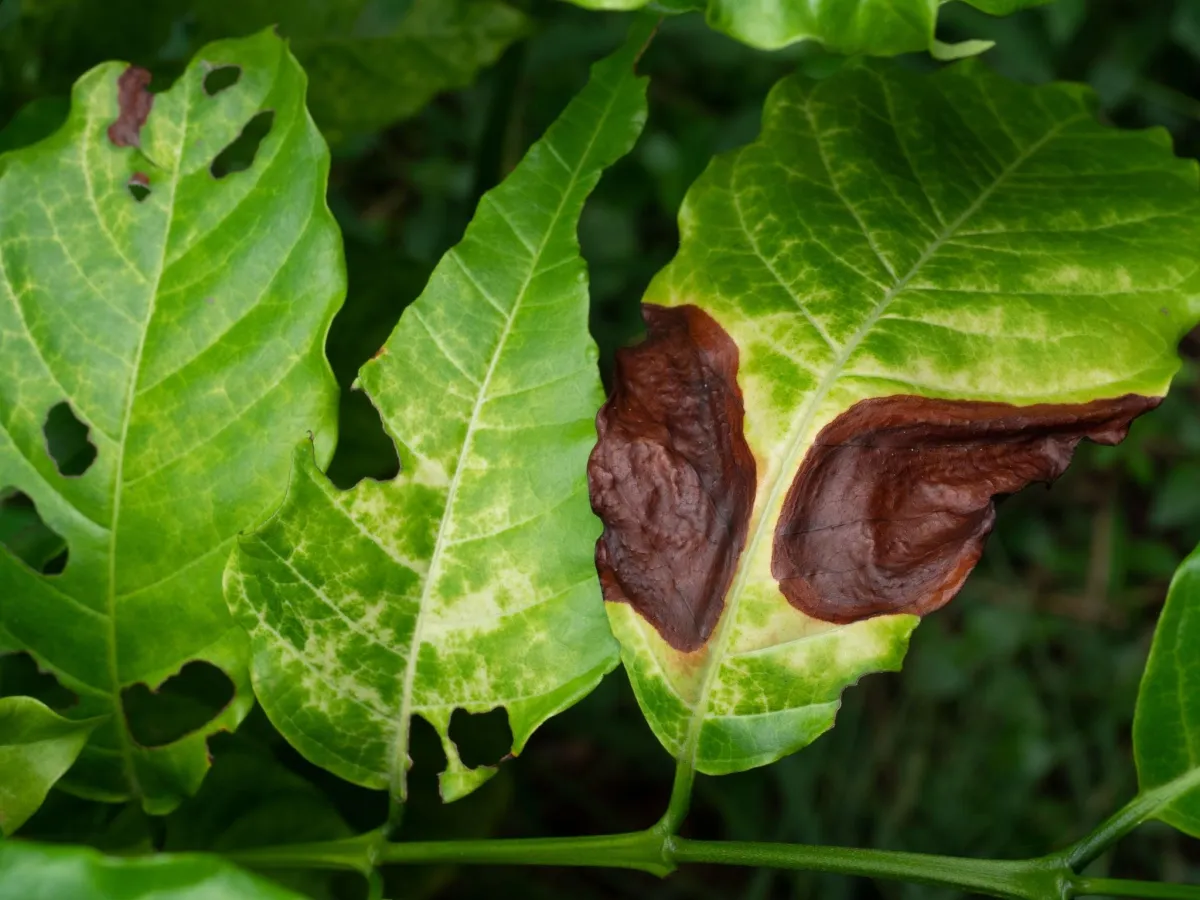

This fungal disease affects many hardwood trees in Louisville, such as sycamore, ash, and maple. Symptoms include dark, water-soaked lesions on leaves, stems, and fruits. Severe infections can lead to defoliation.
Prevention tips:
Fungicide Applications:
Early spring applications can help protect new growth from severe infections.
Clean Up Debris:
Like with apple scab, removing infected leaves and debris can reduce fungal spores.
Improve Tree Vitality:
Regular watering, mulching, and proper fertilization can help improve tree resistance to disease.
Dutch Elm Disease
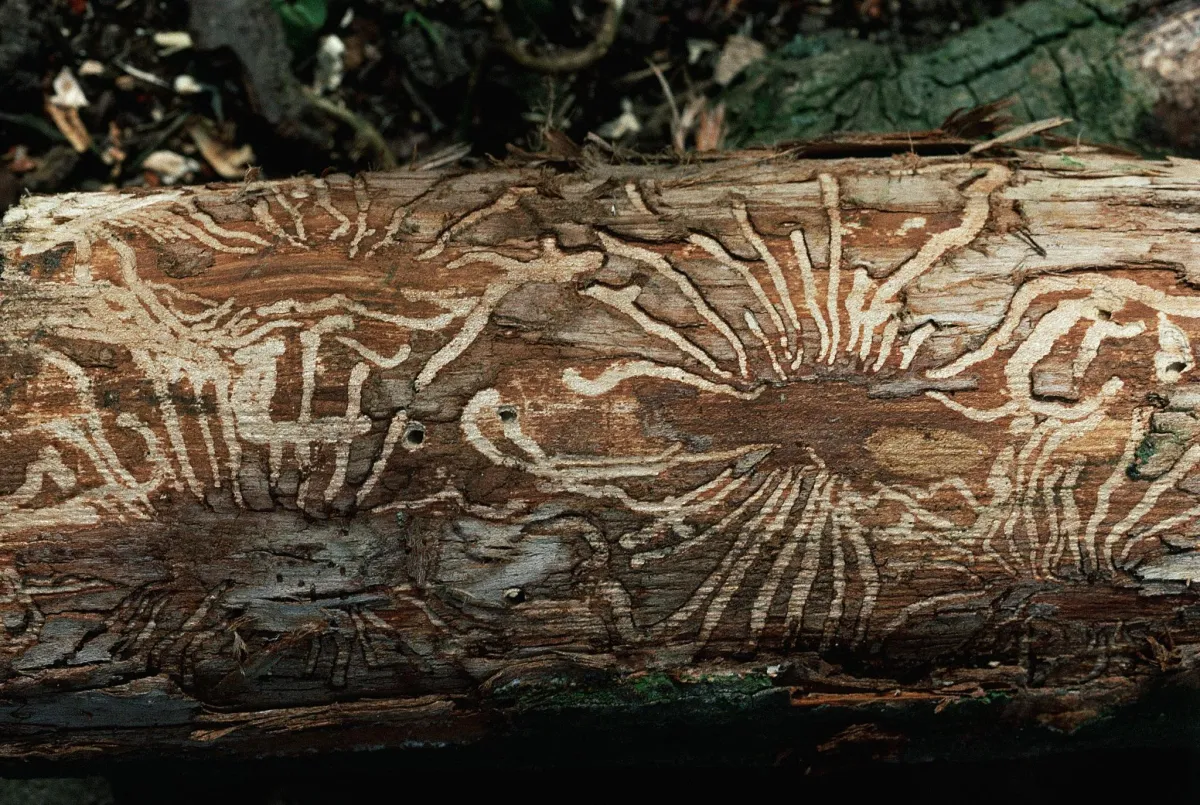

Dutch Elm Disease is a devastating fungal disease that affects elm trees. It is caused by fungi Ophiostoma ulmi and Ophiostoma novo-ulmi. Symptoms include yellowing and wilting of leaves, which begin on one branch and rapidly spread throughout the tree. Infected trees often exhibit a characteristic "flagging" or browning of branches.
Prevention tips:
Prune During Dormancy:
To prevent the spread of the disease, prune only during the dormant season when beetles that spread the fungus are inactive.
Sanitize Tools:
Always sanitize pruning tools between cuts and trees to prevent transferring the fungus from infected trees to healthy ones.
Remove Infected Trees:
Prompt removal of infected trees, along with their stumps and roots, is crucial to prevent the spread of the disease.
Apply Fungicide Treatments:
Preventative fungicide injections by a certified arborist can protect healthy trees, especially in areas where Dutch Elm Disease is common.
Fire Blight
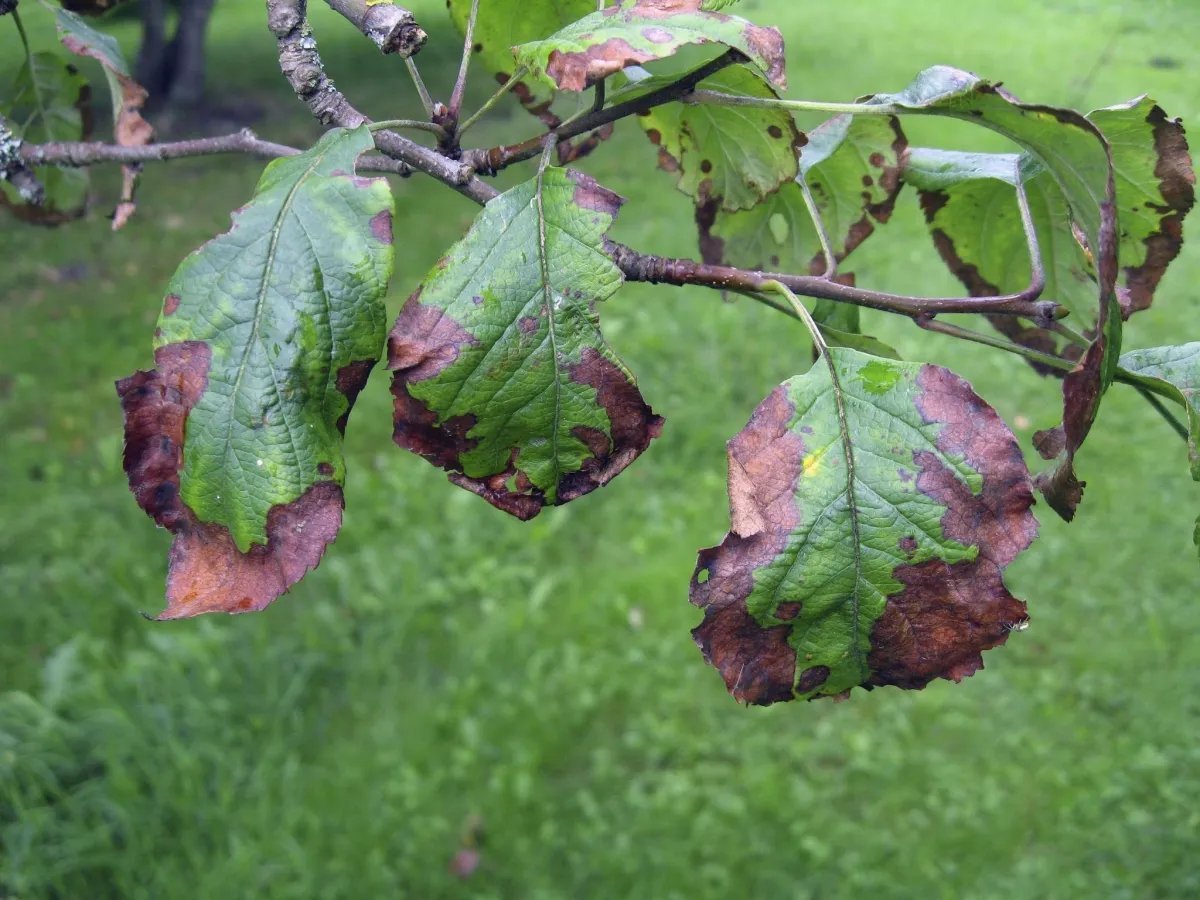

Fire Blight is a bacterial disease that primarily affects pear, apple, and some ornamental trees like crabapples and hawthorns. The disease is caused by the bacterium Erwinia amylovora. It manifests as scorched-looking, blackened leaves, branches, and fruit, giving the appearance that parts of the tree have been burned by fire. The infection can spread rapidly in warm, moist conditions, leading to extensive damage.
Prevention tips:
Resistant Varieties:
Choose tree varieties that are known to be resistant to fire blight, which can significantly reduce disease incidence.
Prune Infected Parts:
Remove any infected branches during the dormant season to prevent the spread of the disease. Make sure to cut well below the visibly affected areas.
Avoid Excess Nitrogen:
Limit the use of high-nitrogen fertilizers as they promote the lush growth of shoots, which are particularly vulnerable to infection.
Sterilize Pruning Tools:
Always sterilize pruning tools with bleach or alcohol between cuts to avoid spreading the bacterium.
Verticillium Wilt
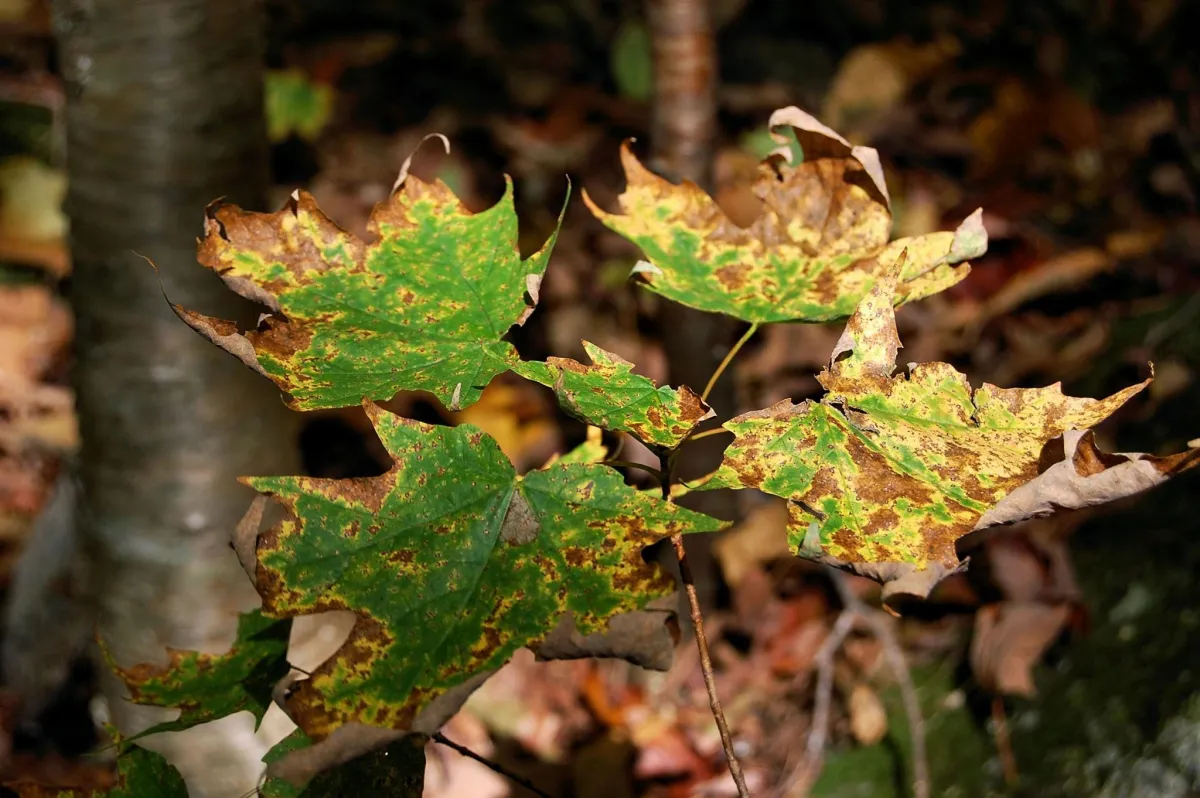

Verticillium Wilt is caused by soil-borne fungi Verticillium dahliae and Verticillium albo-atrum. This disease affects a wide range of trees, including maples, ash, and elm. Symptoms include yellowing and wilting of leaves, often on one side of the tree first, followed by gradual decline and sometimes death of the tree. The fungus affects the tree's vascular system, blocking the flow of water and nutrients.
Prevention tips:
Good Cultural Practices:
Ensure trees are well-watered during dry periods, mulch adequately, and avoid wounding the trees as injuries can provide entry points for the fungus.
Soil Management:
Since the fungus lives in the soil, replacing the soil around the base of the tree or treating it with fungicides can help reduce the risk of infection.
Remove and Replace:
Infected trees and surrounding soil should be removed to prevent the spread of the disease. Consider replacing them with species that are not susceptible to Verticillium wilt.
Noticed any of these signs on your trees?

Written By: Author
Brief author description goes here. harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.





Up Next >
Up Next >
Contact Us
Service Hours
Social Media
Looking for landscaping, lawn care, or other home services?
Contact Us
+1 502-483-0511
Prospect, Louisville, KY 40222
Service Hours
Mon- Fri: 9am - 5pm
Sat & Sun: Appt Only
Social Media

2026 | Apex Pros | Rights Reserved










